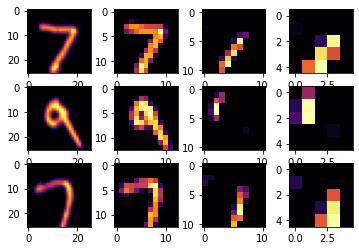What we are tying to accomplish by applying the filter to the original array is that we are changing the numerical value of each pixel. When you are applying filters you are trying to emphasize certain patterns that you want your computer to pick up on to categorize images.
filter = [ [0, 1, 0], [1, -4, 1], [0, 1, 0]]
This filter put a lot of emphasis on vertical lines

filter = [ [5, 1, 0], [1, -4, 1], [-5, 1, 0]]
This filter emphasizes both vertical and horizontal lines

filter = [ [10, 0, 0], [-5, -0, -5], [-7, 7, 0]]
This filter puts emphasis on the all lines and the people walking up the stairs.

In 2x2 array it is doing max pooling, and picking the pixels from largest to smallest. Max pooling helps overfitting.
filter = [ [10, 0, 0], [-5, -0, -5], [-7, 7, 0]] 2x2 array
This filter brings out people and lines the most

For the MNIST dataset. After comparing the DNN and CNN, the CNN performed better. The highest CNN I got was 0.991 while the DNN was 0.977. As I increased the convolutions it took longer on average the accuracy decreased. The plot below is of a CNN with .988 accuracy and a loss of 0.0498 and each epoch took 4 seconds to complete.